What is MVP Development?
In the startup world, the term MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) has become a buzzword. MVPs is the most basic version of a product, having only the essential features needed to solve a specific problem and offer users immediate value. It’s a beginning point to test your idea in the real marketplace with the least amount of time, money, and efforts; it’s not a finished or polished product. The main purpose of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is to validate your idea by seeing how actual users interact with it.This enables innovators to evaluate whether their product actually meets customer needs before investing heavily in full-scale development.
Minimum Viable Product is crucial for startups because it allows founders to test their ideas quickly and cost-effectively before investing heavily in full development. Entrepreneurs can validate their business idea by merely developing the most essential features, obtain real customer feedback, and determine consumer demand early on. It helps businesses attract early users, launch more swiftly, and collect valuable data that determines the product’s future.
MVP Development also demonstrates that the idea has practical traction, making it a powerful evidence of concept for possible partners and investors. By using user-driven development and continual improvement, MVPs are basically the best way for businesses to learn, adapt, and expand. They transform an innovative idea into a profitable, scalable product. Still, a lot of founders struggle with MVP development since they don’t know what an MVP is.
Common Reasons Why Founders Fail in MVP Development
Developing an MVP may seem straightforward, but many startups stumble along the way. Understanding why founders fail can help you avoid the same mistakes. Here are the most common reasons, explained in detail:
Lack of Clear Vision and Strategy
A startup without a clear vision is like a ship sailing without a compass. Founders often jump straight into building without defining the problem they are solving or the value they want to deliver. This leads to scattered features, inconsistent messaging, and a product that doesn’t resonate with users. A clear strategy ensures that every decision, from design to marketing, aligns with the ultimate goal.
Ignoring Market Research
Skipping market research is like building a product in a vacuum. Founders may assume they understand user needs, but without data, they risk launching a product nobody wants. Market research including competitor analysis, surveys, and interviews provides insights into customer pain points, market demand, and pricing strategies. This reduces guesswork and increases the likelihood of success.
Poor Team Collaboration and Communication
MVPs development requires close alignment between developers, designers, marketers, and product managers. When communication breaks down, tasks overlap, deadlines are missed, and the final product suffers. Effective collaboration ensures everyone understands goals, responsibilities, and priorities, leading to smoother development and higher-quality outcomes.
Neglecting User Feedback
An MVP’s main goal is to collect feedback from actual users. One of the main reasons why many startups fail is that they ignore feedback. Founders who skip this step may continue building features based on assumptions rather than real needs. Finding customer problems, improving functionality, and modifying tactics to satisfy market demands are all made easier when users are actively listened to.
Insufficient Budget Planning
Many startups underestimate the costs associated with development, testing, and marketing. Running out of funds before validating the MVP can halt progress and leave potential opportunities unrealized. Proper financial planning, including a buffer for unexpected expenses, ensures the startup can survive the MVP stage and continue iterating.
Choosing the Wrong Technology Stack
Choosing the incorrect technology can lead to long-term issues. Tools that are complicated, outdated, or non-scalable might hinder development, raise expenses, and make changes more challenging in the future. Founders should choose technologies that align with MVP goals, allow rapid iteration, and scale as the product grows, balancing speed, cost, and flexibility.
Lack of Iterative Testing
Many founders release their MVP and consider the job done. However, MVPs are experiments that require continuous testing, learning, and iteration. By analyzing user behavior and feedback, startups can make data-driven decisions, improve functionality, and gradually build a product that truly fits market needs.
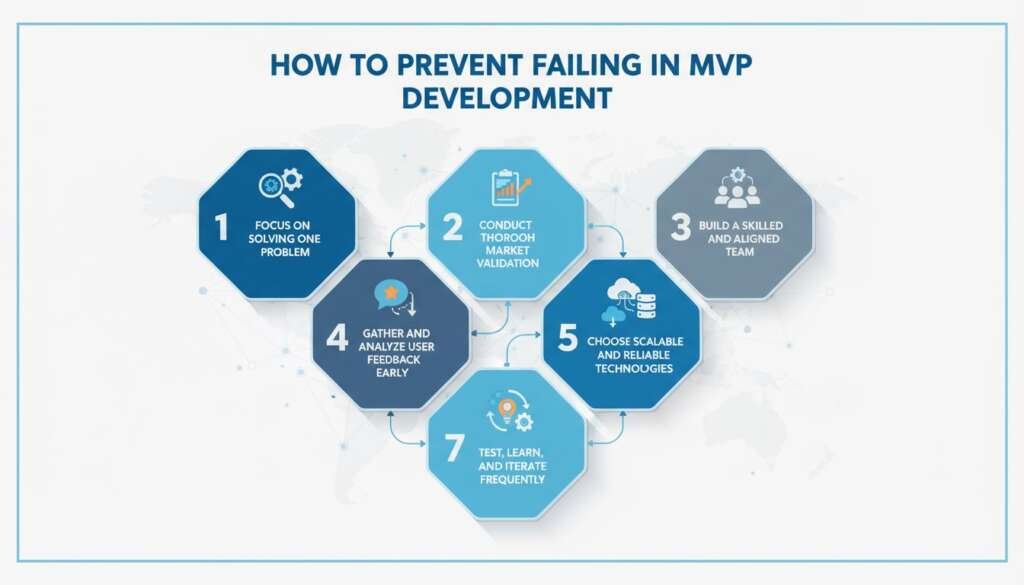
How to Prevent Failing in MVP Development
Launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) can be the turning point for any startup — but it’s also where many founders stumble. From unclear goals and poor market validation to overcomplicating features, even small mistakes can derail your vision. To ensure your MVP stands out and actually delivers value, it’s crucial to take a strategic, data-driven approach right from the start. Building a successful MVP development services requires careful planning, focus, and adaptability. Here are some proven strategies to help founders avoid common pitfalls and increase the chances of success:
Focus on Solving One Core Problem
An MVP should address a single, well-defined problem rather than trying to fix everything at once. By concentrating on one primary pain point, founders can deliver meaningful value to users quickly. Solving one problem well often leads to stronger adoption than attempting multiple features half-heartedly.
Conduct Thorough Market Validation
It’s critical to comprehend your target market. Before starting full production, confirm demand using websites, interviews, surveys, and short pilot tests. Market validation guarantees that your MVP satisfies actual user needs and lowers the danger of creating a product that no one wants.
Build a Skilled and Aligned Team
A startup’s success depends on its team. Ensure your developers, designers, and marketers understand the vision, share priorities, and communicate effectively. A small, aligned, and skilled team is more productive and capable of quickly iterating on feedback.
Gather and Analyze User Feedback Early
Start collecting user feedback as soon as the MVP is in users’ hands. To determine problems, measure satisfaction, and find areas for improvement, use surveys, analytics, and interviews. Early insights help refine the product and guide development in the right direction.
Plan Finances and Resources Strategically
Budget wisely for development, testing, marketing, and iteration. Allocate resources carefully and include a contingency for unexpected challenges. Strategic financial planning ensures the MVP can reach validation without exhausting funds prematurely.
Choose Scalable and Reliable Technologies
Select technologies that are scalable, dependable, and adaptable. Avoid overly complex or outdated stacks that might hinder future growth or progress. As the product develops, the appropriate technology promotes growth, reduces technical debt, and enables quick iterations.
Test, Learn, and Iterate Frequently
Treat your MVP as a living experiment. Continuously test features, measure results, and refine based on feedback. Frequent iterations allow the product to evolve in alignment with user needs, helping you achieve product-market fit faster.
Final Tips for Building a Successful MVP
Building a successful MVP is as much about strategy and mindset as it is about coding. Here are some final tips to ensure your MVP achieves its purpose and sets a strong foundation for growth:
- Start small with one main feature.
- Test your idea before building fully.
- Focus on learning, not perfection.
- Listen to user feedback.
- Make quick improvements often.
- Track important user metrics.
- Stay flexible and adapt as needed.
Conclusion
Founders often fail in MVP development startups due to a combination of lack of clear vision, overcomplicating the product, ignoring market research, poor team collaboration, and neglecting user feedback. These common mistakes can lead to wasted time, resources, and missed opportunities. However, failure is not inevitable.
Founders can significantly improve their chances of success by establishing specific, quantifiable goals, concentrating on resolving a single issue, validating the market, keeping the MVPs simple, assembling a talented team, gathering feedback early, making prudent financial plans, selecting the best technology, iterating often, and remaining adaptable. The key is to treat the MVP as a learning tool, not a finished product, and to continuously adapt based on real user insights. By following these strategies, founders can avoid common pitfalls, build products that meet real needs, and lay the foundation for long-term growth and success.