The logistics industry is transforming faster than ever before — and automation is leading that change. In a world where customers expect faster deliveries, real-time tracking, and error-free service, traditional manual operations simply can’t keep up. Every missed entry in a spreadsheet or delayed communication can translate into lost clients and higher costs. From freight forwarding paperwork to warehouse inventory management and last-mile delivery coordination, logistics teams still spend countless hours on repetitive tasks. These manual routines not only slow down performance but also make it harder to scale efficiently. As competition grows and margins shrink, companies that continue to rely on outdated systems are falling behind.
That’s where logistics automation comes in. By integrating smart software, IoT devices, and digital workflows, businesses can replace manual steps with seamless automated processes. Whether it’s tracking shipments in real-time, generating digital invoices automatically, or optimizing delivery routes using data — automation can save time, reduce errors, and improve customer satisfaction.
What’s even better is that automation is no longer limited to global logistics giants. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) across Pakistan and other emerging markets can now adopt affordable automation tools designed specifically for freight forwarders, warehouse operators, and transport fleets.
This blog dives deep into five practical automation ideas of 2025 that you can start implementing right away. Each section explains a real-world logistics problem, the automation solution available, and a step-by-step guide to manually convert your existing processes into digital systems. Whether you manage shipments, run a warehouse, or oversee a delivery fleet — this guide will help you understand where to start, how to adapt, and how to achieve measurable improvements in speed, accuracy, and profitability.
What is Automation?
Automation is the process of using technology — such as software, machines, or digital systems — to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Instead of doing repetitive or manual work yourself, automation allows computers, sensors, or programs to handle it automatically based on pre-set rules or data inputs.
In simple terms, automation means letting technology do the routine work for you, so your team can focus on strategy, decision-making, and customer service.
For example:
- In logistics, automation can send shipment updates automatically to clients instead of manually emailing each one.
- In warehousing, scanners or robots can automatically update inventory levels when items are received or dispatched.
- In fleet management, GPS systems can automatically track vehicles and alert managers about maintenance or route delays.
Why Automation Matters
Automation helps businesses:
- Save time by reducing manual data entry and repetitive tasks
- Improve accuracy by minimizing human errors
- Increase efficiency with faster, more consistent processes
- Enhance decision-making through real-time data visibility
- Cut costs by optimizing operations and reducing waste
In short, automation transforms how a business runs — it replaces outdated, manual workflows with intelligent, self-operating systems that improve both speed and reliability.
5 Automation Ideas For Logistics Businesses
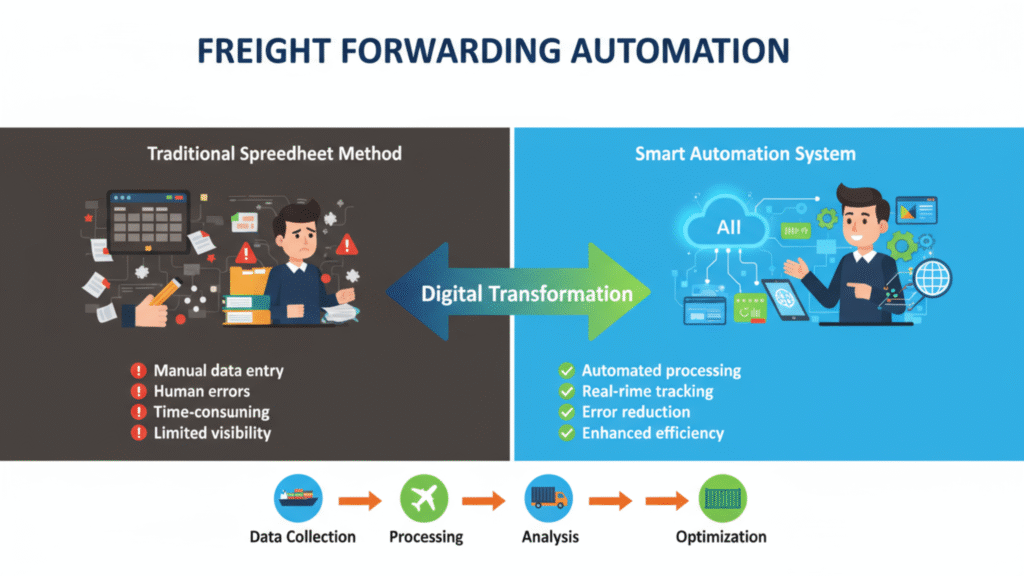
1. Freight Forwarding Automation — Replacing Spreadsheets with Smart Systems
Freight forwarding is at the heart of global logistics. It’s the bridge that connects exporters, importers, shipping lines, customs agents, and transporters — all working together to move goods across borders safely and on time. But while the logistics world has advanced with digital tracking and e-commerce growth, many freight forwarders still rely on outdated manual methods to manage their operations. From rate management and shipment booking to documentation and customer communication, almost every step in freight forwarding involves paperwork and manual coordination.
Teams often spend hours managing Excel sheets, searching through emails for rate confirmations, and printing customs documents. Each small mistake — a wrong HS code, a missing invoice, or a mistyped number — can cause shipment delays, customs fines, or even loss of business.
As freight volumes increase, this manual way of working becomes harder to sustain. Clients expect faster responses, live shipment tracking, and error-free billing. Competing in this fast-paced environment using only spreadsheets and emails is like trying to run a modern airline with a typewriter.
That’s why automation is becoming a game-changer for freight forwarders. Instead of juggling multiple tools and papers, freight forwarding software brings everything into one digital platform — from quotations to cargo tracking. It helps small and medium logistics companies become more organized, faster, and ready to serve modern customers who expect transparency and speed.
The problem with manual work
Freight teams often use spreadsheets and printed invoices to track everything. They send rates through emails, fill in data by hand, and store documents in physical folders. It takes time to find the right file, and one typing error can cause delays or even financial loss.
The automated approach
Freight forwarding software helps remove repetitive manual work. These systems can automatically generate quotations, store shipment details in one place, and track cargo in real-time. Some software even sends automatic updates to clients when their shipment reaches a certain stage.
Popular freight systems like CargoWise, ShipThis, and GoFreight already offer these features.
How to move from manual to automated
- Make a list of every task you currently do manually, from rate requests to delivery updates.
- Select software that can handle most of these steps automatically.
- Convert your paper documents into digital files and store them in a single online system.
- Set simple rules — for example, when a booking is confirmed, the system should automatically send the invoice.
- Train your team on how to use the new tools confidently.
A freight forwarding company in Karachi adopted digital freight software and managed to reduce its quotation preparation time from two days to just a few hours.
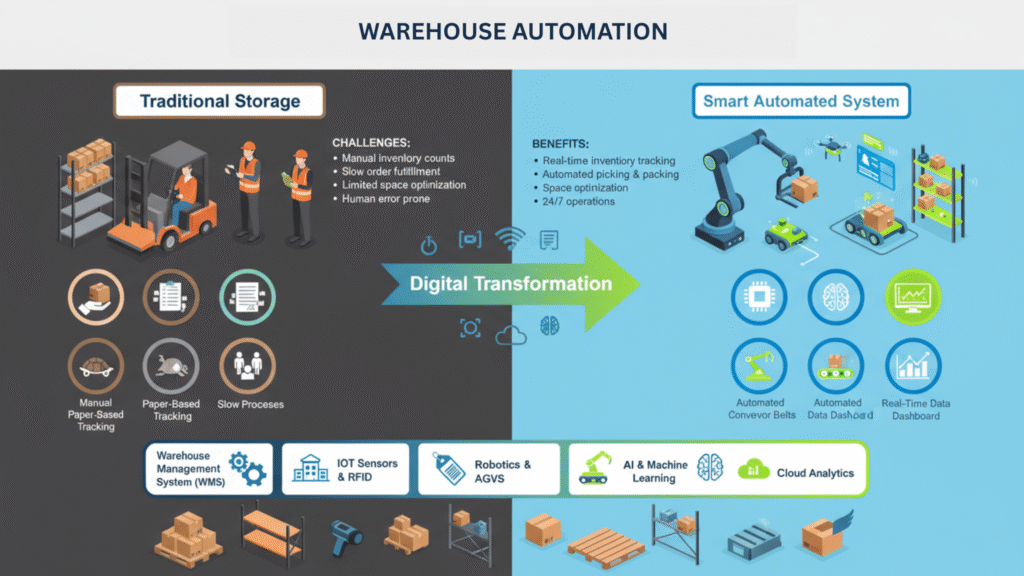
2. Warehouse Automation — Turning Storage into a Smart System
In many warehouses, employees still walk around with clipboards or record numbers by hand. This causes mistakes in stock counts and delays in deliveries. Every miscount or misplaced item can have a ripple effect — slowing down order fulfillment, creating stockouts, and frustrating customers who expect their goods on time.
Warehouses today often handle thousands of SKUs, ranging from raw materials to finished goods. Manually tracking each item not only wastes time but also increases the chances of human error. Staff spend hours verifying inventory, generating pick lists, and updating records, leaving little room to focus on improving warehouse efficiency or responding quickly to urgent orders.
Moreover, as businesses scale, the volume of inventory moves faster than humans can reliably track. Without a proper system, overstocking or running out of critical items becomes common, leading to lost sales or unnecessary storage costs. Traditional warehouse operations struggle to keep up with real-time demands, making manual processes a bottleneck rather than a support system.
This is where warehouse automation comes into play. By integrating digital systems like Warehouse Management Software (WMS) with barcodes, RFID tags, and inventory tracking tools, warehouses can operate more accurately and efficiently. Automation helps keep stock counts precise, optimizes the placement of goods, and allows staff to focus on higher-value tasks such as quality checks and timely dispatch. With the right automation, warehouses transform from error-prone manual systems into smart, self-updating hubs, capable of handling high volumes with speed and reliability.
The problem with manual warehouse operations
Manual recordkeeping often results in inaccurate stock numbers. Items may be misplaced, overstocked, or even lost. Workers spend time looking for goods, and orders are delayed when the stock information isn’t up to date.
The automated approach
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) can make a big difference. It can track every product using barcodes or RFID tags, automatically update stock levels, and suggest where to place items for faster picking. It also generates reports on what’s running low or what’s overstocked.
How to switch to automation
- Review how goods currently move in and out of your warehouse.
- Choose a warehouse system that suits your business size and budget.
- Start using barcodes or RFID tags on all items.
- Connect the system to your other business software, like accounting or freight systems.
- Measure improvements regularly — such as fewer stock errors or faster order completion.
One warehouse in Lahore introduced RFID tracking and improved its stock accuracy to almost 100%, saving many hours each week on manual counting.
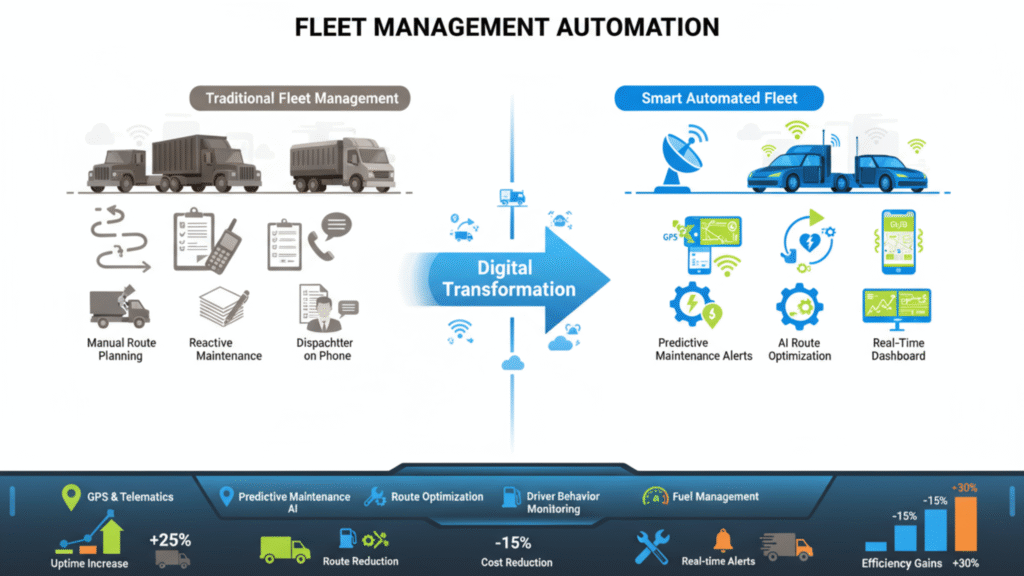
3. Fleet Management Automation — Smarter Vehicles, Less Downtime
Managing a fleet of vehicles is difficult when done by hand. It’s not easy to track where every driver is, how much fuel is being used, or when maintenance is due. Relying on phone calls, paper logs, or spreadsheets often leads to delays, missed maintenance schedules, and higher operating costs.
Fleet managers need real-time visibility to ensure vehicles are used efficiently, deliveries stay on schedule, and fuel and maintenance expenses are controlled. Manual tracking makes it almost impossible to identify patterns like idle time, frequent route delays, or inefficient fuel consumption.
Automation solves these challenges by combining GPS tracking, telematics, and digital reporting into one system. Fleet management tools provide live location updates, fuel and mileage monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, and route optimization. With these insights, managers can reduce downtime, save fuel, and improve overall fleet performance without the constant back-and-forth calls or paperwork.
The problem with manual tracking
Fleet managers often call drivers for updates, note down mileage on paper, and forget to schedule maintenance on time. This leads to fuel waste, longer delivery times, and vehicle breakdowns that could have been avoided.
The automated approach
Fleet management systems solve these problems using GPS tracking, sensors, and telematics. These tools show real-time vehicle locations, track fuel usage, alert you when maintenance is due, and even suggest better routes.
With automation, you can monitor all your vehicles from one dashboard instead of dozens of calls and papers.
How to move to automation
- Start by installing GPS trackers on your most active vehicles.
- Choose software that fits your fleet size and offers maintenance alerts.
- Replace paper driver logs with a mobile app.
- Let the system generate reports automatically instead of doing it manually.
- Use route optimization to save time and fuel.
A transport company in Pakistan reduced fuel costs by 15% and improved on-time delivery by switching to automated fleet tracking and route planning.
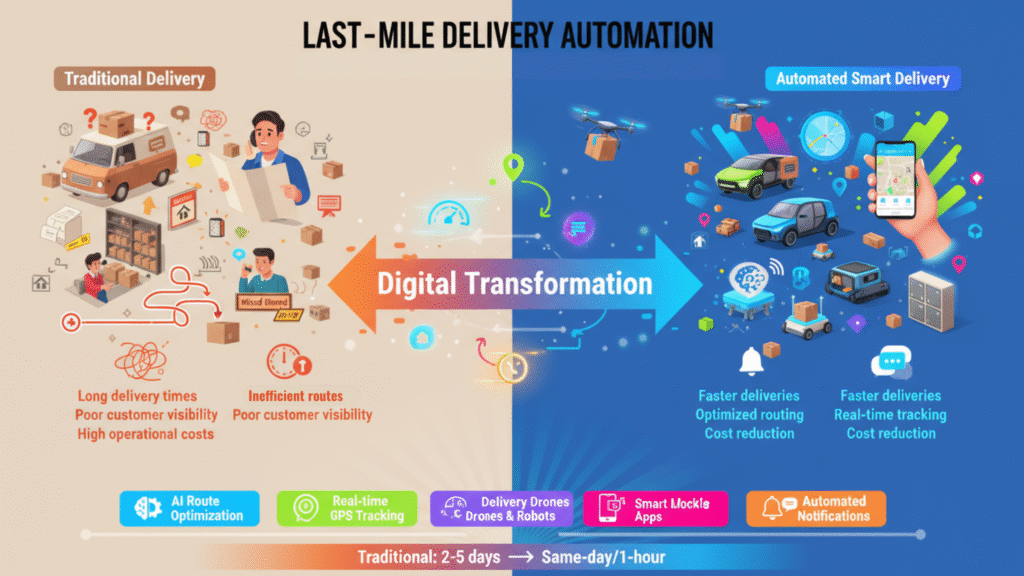
4. Last-Mile Delivery Automation — The Key to Faster Deliveries
The “last mile” is the final stage of delivery — when goods move from the warehouse to the customer’s door. It is often the most expensive and complicated part of logistics, especially with the rise of online shopping. Manual coordination at this stage can lead to missed deliveries, confused drivers, and frustrated customers. Dispatchers who assign routes by hand, call customers for directions, and track drivers through phone updates often face delays and errors. This not only slows deliveries but also increases operational costs and reduces customer satisfaction.
Automation helps simplify last-mile logistics by digitally assigning drivers, optimizing routes, and providing real-time tracking. Customers can receive live updates, while managers monitor performance and delivery progress from a single platform. By reducing manual intervention, companies can deliver faster, cut costs, and provide a more reliable service.
The problem with manual coordination
Many dispatchers still assign drivers manually, call customers for addresses, and keep checking where each package is. This leads to confusion, delays, and unhappy customers.
The automated approach
Last-mile delivery software makes this process simple. It automatically assigns drivers, plans the best routes, and sends customers real-time updates. Delivery agents can also upload proof of delivery, such as an e-signature or a photo.
How to switch from manual to automated
- Make sure all delivery requests are entered digitally from your website or order system.
- Choose a delivery management platform that connects with your existing tools.
- Use automated route planning to save fuel and time.
- Enable tracking links so customers can see where their order is.
- Review reports regularly to improve performance.
A courier company in Karachi introduced automated delivery tracking and reduced delivery times by 25%, while customer satisfaction improved noticeably.
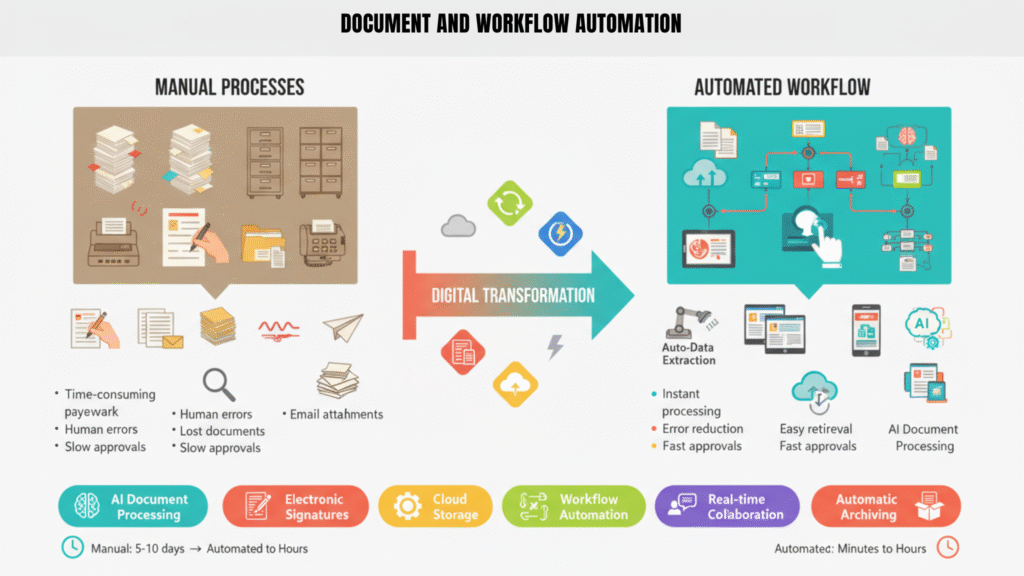
5. Document and Workflow Automation — Saving Time Behind the Scenes
Even if your freight, fleet, or warehouse systems are automated, paperwork can still slow you down. Many logistics companies still rely on printed invoices, bills of lading, delivery notes, and signed forms, which take time to manage, file, and retrieve. Manual document handling not only consumes valuable staff hours but also increases the risk of lost or misplaced files.
Delays in paperwork can slow down billing, customer responses, and compliance processes. For example, waiting for a signed delivery receipt or manually routing invoices for approval can add days to your operations. This creates bottlenecks that affect cash flow, customer satisfaction, and overall efficiency.
Document and workflow automation solves these challenges by converting manual paper processes into digital workflows. Using simple tools or platforms, businesses can automatically generate invoices, route documents for approval, and store files securely in the cloud. E-signatures replace physical signatures, and automated notifications ensure that nothing gets stuck waiting for human action.
By digitizing and automating document workflows, logistics teams can reduce errors, save time, and speed up critical processes like billing, reporting, and compliance. Staff can focus on higher-value tasks instead of chasing paperwork, and managers gain better visibility into operational workflows.
Automation of document and workflow processes turns back-office operations from a slow, error-prone task into a fast, organized, and reliable system — supporting the entire logistics chain efficiently.
The problem with paper-based work
Paper documents can get lost, take days to move between departments, and delay payments. Manual paperwork also increases the risk of compliance mistakes.
In addition, tracking approvals, signatures, and updates on physical documents requires constant follow-up, which wastes time and effort. Employees spend hours locating files, verifying information, and manually entering data into systems, leaving less time for strategic tasks.
These inefficiencies not only slow down operations but can also affect cash flow, customer satisfaction, and overall productivity. For logistics businesses, where timely processing is critical, relying on paper-based workflows can become a major bottleneck.
The automated approach
Document and workflow automation replaces these steps with digital versions. With tools like DocuWare or Microsoft Power Automate, you can create digital templates for invoices, route them for approval, and store them safely online. You can even add e-signatures for instant approval.
How to switch
- Identify which document processes take the most time.
- Create digital templates for them.
- Connect your document system with your other business tools.
- Automate who gets what document when.
- Encourage staff to use e-signatures and cloud storage instead of printing.
A logistics company in Lahore automated its billing and reduced invoice processing time from three days to just a few hours, making cash flow smoother.
Starting Your Automation Journey
If your logistics company still relies heavily on spreadsheets, phone calls, or paper, it’s time to start your automation journey. You don’t need to automate everything at once. Begin with one area — for example, freight forwarding or warehouse management — and expand as your team gets comfortable.
Here’s a simple way to start:
- Identify the tasks that take up most of your team’s time.
- Pick one area that would benefit most from automation.
- Research tools that are affordable and easy to use.
- Train your staff and make sure they understand the benefits.
- Track your progress and improve as you go.
Automation is not about replacing people. It’s about helping them work faster, make better decisions, and focus on what really matters — delivering great service.
Final Thoughts
Automation is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s a practical necessity for logistics businesses of all sizes. From freight forwarding and warehouse operations to fleet management, last-mile delivery, and document handling, automating repetitive tasks can save time, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency.
The key to successful automation is starting small and scaling gradually. You don’t need to automate everything at once. Identify the areas that consume the most time or are prone to errors, and begin with simple tools that your team can adopt easily. As your staff becomes comfortable with automated systems, you can expand automation to other processes.
It’s also important to remember that automation is not about replacing people. It’s about empowering teams to focus on higher-value tasks, such as decision-making, problem-solving, and improving customer service. By taking over repetitive, time-consuming work, automation allows your employees to contribute more strategically to the growth of the business.
Finally, implementing automation helps logistics companies stay competitive in a fast-paced market. Faster shipments, accurate inventory, optimized routes, and seamless documentation lead to satisfied customers, lower costs, and better overall performance. By embracing automation, logistics businesses can operate smarter, scale faster, and focus on what really matters — delivering exceptional service.
